12 Ways Nutrient Density Transforms Everyday Eating
1. What Is Nutrient Density and Why It Matters

Nutrient density refers to the concentration of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients in a food compared to its calorie content. Foods high in nutrient density provide more health benefits without excess calories, making them essential for maintaining overall wellness. Choosing nutrient-dense foods supports strong immunity, healthy skin, and balanced energy levels throughout the day.
Incorporating nutrient-dense foods into daily meals can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. Understanding nutrient density helps you make smarter choices, ensuring that every bite counts toward better health rather than empty calories.
2. The Science Behind Nutrient Density
The concept of nutrient density is grounded in nutritional science, focusing on the ratio of nutrients to calories in food. Foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants but low in calories are considered highly nutrient-dense. Examples include leafy greens, berries, lean proteins, and whole grains, which deliver maximum nutrition with minimal energy intake.
Research shows that consuming a diet rich in nutrient-dense foods optimizes metabolism, improves body function, and supports long-term health. It emphasizes quality over quantity, encouraging individuals to prioritize foods that enhance nutrient intake without contributing to excess calorie consumption.
3. How Nutrient Density Impacts Daily Health

Eating nutrient-dense foods daily ensures that your body receives the essential nutrients it needs to function optimally. These foods provide energy, improve immune response, and support mental clarity. Regular intake helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, reduces inflammation, and promotes overall vitality.
Neglecting nutrient-dense foods can lead to deficiencies and poor health outcomes, even if calorie intake is adequate. Focusing on nutrient density rather than just calories empowers smarter food choices, allowing for a balanced diet that promotes both physical and mental well-being.
4. Nutrient Density vs. Calorie Density

Nutrient density and calorie density are often confused but are very different concepts. Calorie-dense foods are high in calories but may provide few nutrients, such as sugary snacks or fried foods. Nutrient-dense foods, in contrast, offer more vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants per calorie, maximizing health benefits.
Choosing nutrient-dense foods over calorie-dense options helps control weight, improves health markers, and reduces the risk of chronic illnesses. By understanding this distinction, you can prioritize foods that fuel your body effectively while minimizing unnecessary calorie intake.
5. Top Nutrient-Dense Vegetables to Include

Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are among the most nutrient-dense vegetables. They are packed with vitamins A, C, K, folate, and minerals like iron and calcium, all while being very low in calories. Adding them to salads, smoothies, or cooked dishes can significantly boost your daily nutrient intake.
Other vegetables such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and bell peppers also provide high levels of antioxidants and fiber. Regularly including a variety of nutrient-dense vegetables supports heart health, digestion, and immune function, making them an essential component of a balanced diet.
6. Fruits That Pack a Nutrient Punch
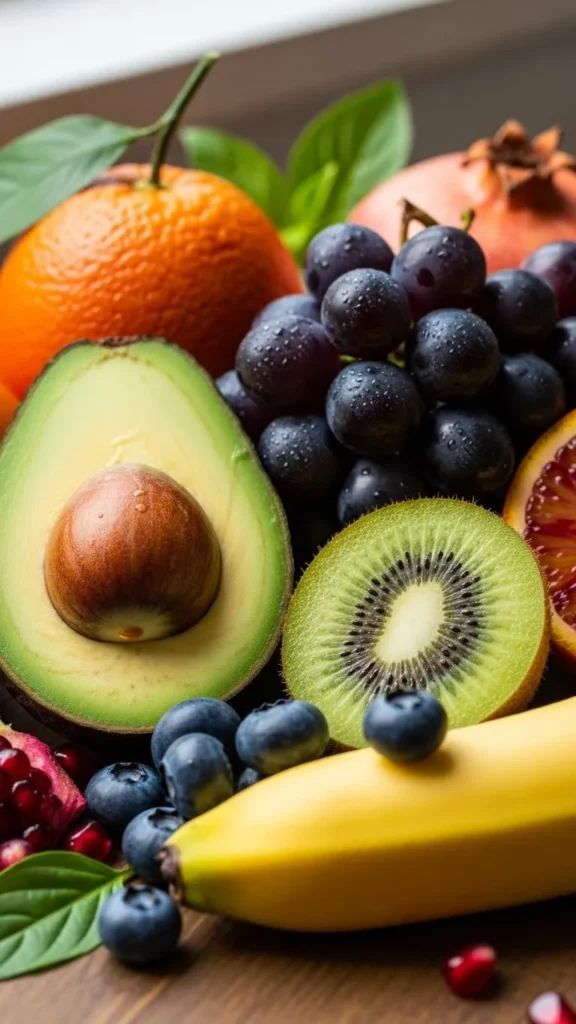

Berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are incredibly nutrient-dense and antioxidant-rich. They are low in calories and high in vitamin C, fiber, and polyphenols, which help combat oxidative stress and support overall health. Including berries in breakfast, snacks, or desserts is a simple way to increase nutrient intake.
Citrus fruits, apples, and kiwis are also excellent sources of essential vitamins and minerals. Consuming a variety of colorful fruits ensures a wide spectrum of nutrients, boosts immunity, and supports energy levels throughout the day.
7. Whole Grains and Their Nutrient Benefits

Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, oats, and barley are nutrient-dense carbohydrate sources. They contain fiber, B vitamins, magnesium, and antioxidants, which contribute to heart health, digestive wellness, and sustained energy. Unlike refined grains, whole grains provide more nutrients per calorie.
Including whole grains in meals helps regulate blood sugar levels and maintain satiety. Replacing refined grains with whole grains is a simple strategy to increase nutrient density while supporting long-term weight management and metabolic health.
8. Protein Sources With High Nutrient Density
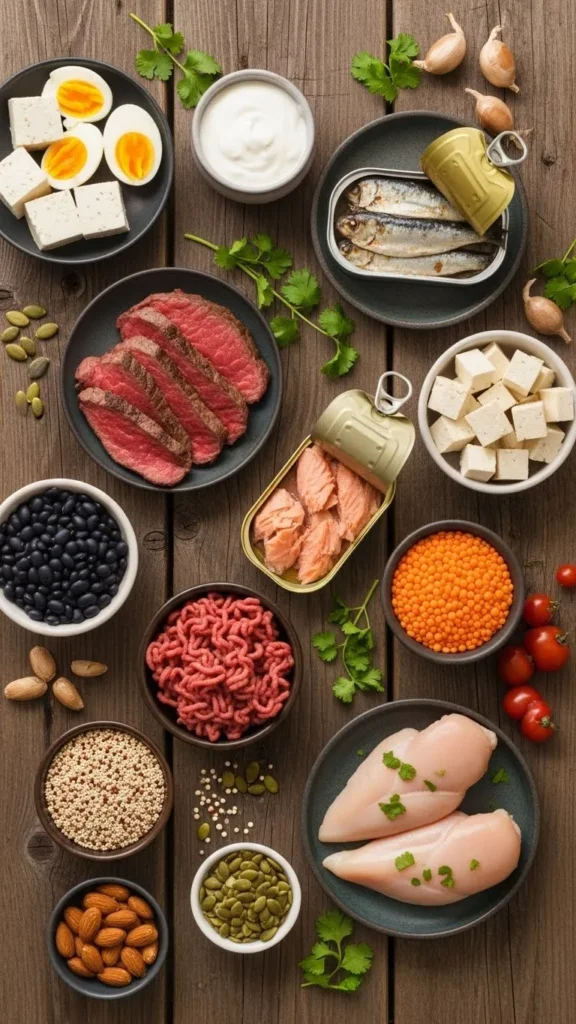

Lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes are nutrient-dense protein sources essential for body repair and growth. Fish like salmon and sardines provide omega-3 fatty acids along with protein, while legumes such as lentils and chickpeas offer fiber and minerals in addition to protein.
Plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and nuts also deliver vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. Incorporating a variety of protein sources enhances nutrient intake, supports muscle health, and helps maintain energy throughout the day, making them a cornerstone of a nutrient-dense diet.
9. Healthy Fats That Boost Nutrient Absorption

Healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are essential for nutrient absorption and overall health. They help your body absorb fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K, while also providing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids that support heart and brain function.
Including these fats in your meals can enhance satiety, stabilize blood sugar, and improve cardiovascular health. Choosing nutrient-dense fat sources over processed oils ensures you get maximum nutritional benefits without unnecessary calories.
10. Dairy and Alternatives: Nutrient-Rich Choices

Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are nutrient-dense sources of calcium, vitamin D, and protein. They help build strong bones, support muscle function, and maintain overall metabolic health. Plant-based alternatives like fortified almond or soy milk also offer essential nutrients while catering to dietary restrictions.
Regular consumption of nutrient-rich dairy or alternatives promotes bone density, aids digestion, and contributes to a balanced diet. Selecting options with minimal added sugars ensures you maximize nutrient intake without excess calories.
11. The Role of Vitamins in Nutrient Density

Vitamins are organic compounds that support critical bodily functions, and they are a key component of nutrient density. Vitamins A, C, D, E, and K, along with the B-complex vitamins, help regulate metabolism, immune function, and energy production. Consuming foods rich in these vitamins ensures overall health and vitality.
A nutrient-dense diet with a variety of colorful fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides a natural supply of essential vitamins, reducing the need for supplementation. Prioritizing vitamin-rich foods improves immunity, cognitive function, and long-term well-being.
12. Minerals That Maximize Food Value
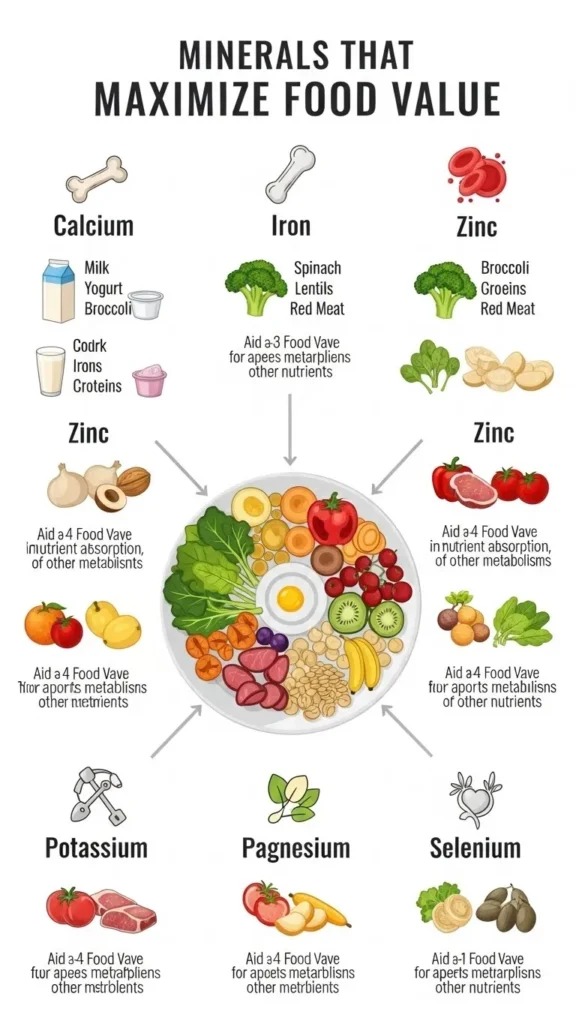
Minerals like calcium, magnesium, iron, potassium, and zinc are vital for body structure, metabolism, and cellular function. They are crucial for bone health, muscle function, and oxygen transport in the blood. Nutrient-dense foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and legumes are excellent sources of these minerals.
Regularly including mineral-rich foods in your diet supports heart health, improves energy levels, and enhances overall body performance. A focus on mineral-rich meals ensures that each calorie consumed delivers maximum nutritional value.
Conclusion
Understanding nutrient density is the key to smarter, healthier eating. By choosing foods rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and protein while keeping calories in check, you can maximize the benefits of every meal. Focusing on nutrient-dense choices supports immunity, energy, brain function, and long-term health.
Incorporating a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your daily diet ensures you get the most nutrition from every bite. Making small, informed changes in meal planning and grocery shopping can transform your eating habits, leading to better health outcomes and a more balanced lifestyle.






